Fillable Printable Stakeholder Analysis Sample Template
Fillable Printable Stakeholder Analysis Sample Template

Stakeholder Analysis Sample Template

Stakeholder Analysis
Winning support for your projects
by Rachel Thompson
"Stakeholder management is critical to the success of every project in every organization I have ever
worked with. By engaging the right people in the right way in your project, you can make a big difference
to its success... and to your career."
As you become more successful in your career, the actions you take and the projects you run will affect
more and more people. The more people you affect, the more likely it is that your actions will impact
people who have power and influence over your projects. These people could be strong supporters of
your work – or they could block it.
Stakeholder Management is an important discipline that successful people use to win support from
others. It helps them ensure that their projects succeed where others fail. Stakeholder Analysis is the
technique used to identify the key people who have to be won over. You then use Stakeholder Planning
to build the support that helps you succeed. The benefits of using a stakeholder-based approach are:
You can use the opinions of the most powerful stakeholders to shape your projects at an early
stage. Not only does this make it more likely that they will support you, their input can also
improve the quality of your project
Gaining support from powerful stakeholders can help you to win more resources – this makes it
more likely that your projects will be successful
By communicating with stakeholders early and frequently, you can ensure that they fully
understand what you are doing and understand the benefits of your project – this means they
can support you actively when necessary
You can anticipate what people's reaction to your project may be, and build into your plan the
actions that will win people's support.
How to Use the Tool:
The first step in Stakeholder Analysis is to identify who your stakeholders are. The next step is to work
out their power, influence and interest, so you know who you should focus on. The final step is to
develop a good understanding of the most important stakeholders so that you know how they are likely
to respond, and so that you can work out how to win their support – you can record this analysis on a
stakeholder map. After you have used this tool and created a stakeholder map, you can use the
stakeholder planning tool to plan how you will communicate with each stakeholder.
Step 1. Identify Your Stakeholders: The first step in your stakeholder analysis is to brainstorm who your
stakeholders are. As part of this, think of all the people who are affected by your work, who have
influence or power over it, or have an interest in its successful or unsuccessful conclusion.
The table below shows some of the people who might be stakeholders in your job or in your projects:

Remember that although stakeholders may be both organizations and people, ultimately you must
communicate with people. Make sure that you identify the correct individual stakeholders within a
stakeholder organization.
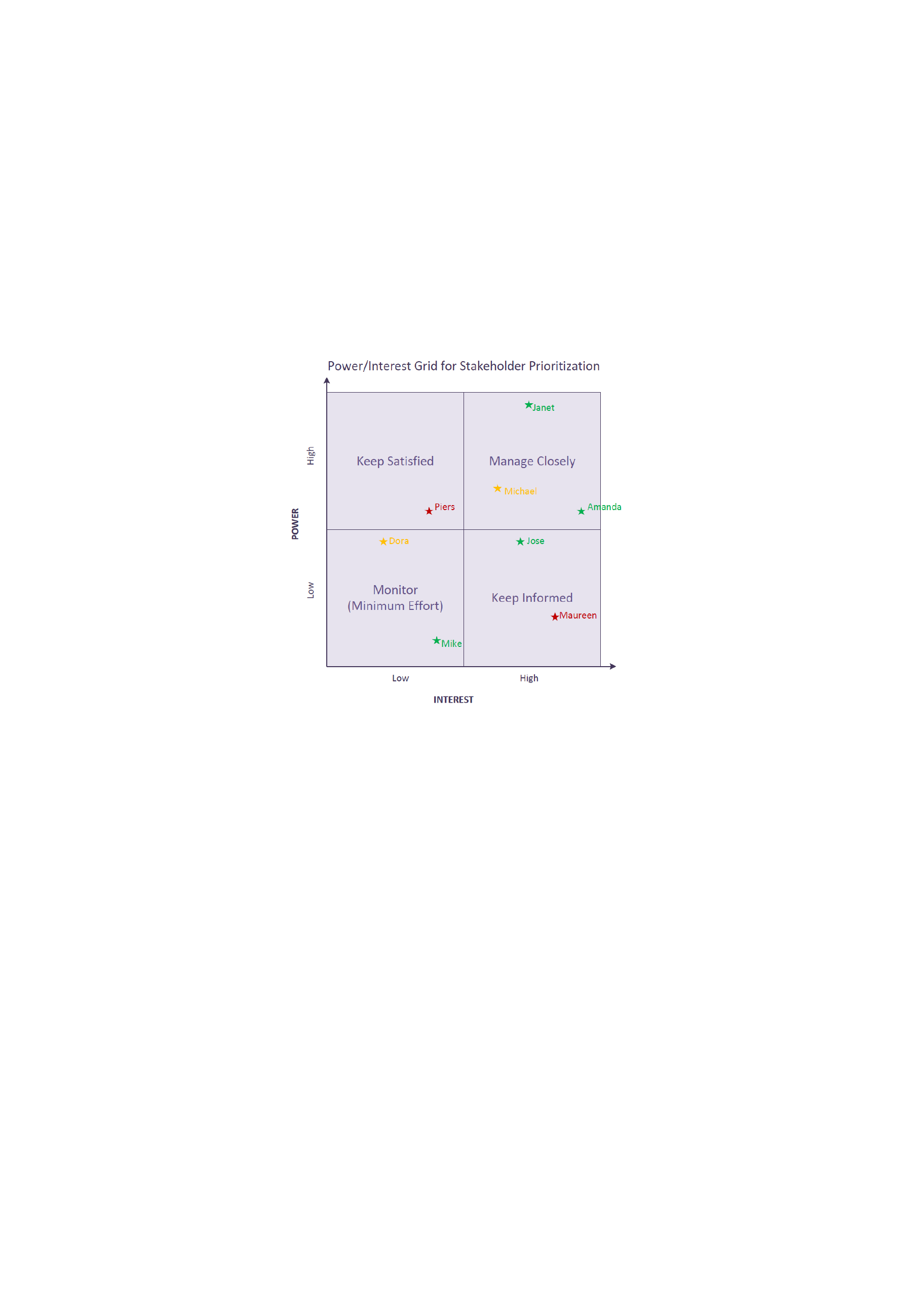
Step 2. Prioritize Your Stakeholders: You may now have a long list of people and organizations that are
affected by your work. Some of these may have the power either to block or advance. Some may be
interested in what you are doing, others may not care. Map out your stakeholders on a Power/Interest
Grid as shown below, and classify them by their power over your work and by their interest in your work.
For example, your boss is likely to have high power and influence over your projects and high interest.
Your family may have high interest, but are unlikely to have power over it. Someone's position on the
grid shows you the actions you have to take with them:
High power, interested people: these are the people you must fully engage and make the
greatest efforts to satisfy.
High power, less interested people: put enough work in with these people to keep them
satisfied, but not so much that they become bored with your message.
Low power, interested people: keep these people adequately informed, and talk to them to
ensure that no major issues are arising. These people can often be very helpful with the detail of
your project.
Low power, less interested people: again, monitor these people, but do not bore them with
excessive communication.
Step 3. Understand Your Key Stakeholders: You now need to know more about your key stakeholders.
You need to know how they are likely to feel about and react to your project. You also need to know
how best to engage them in your project and how best to communicate with them. Key questions that
can help you understand your stakeholders are:
What financial or emotional interest do they have in the outcome of your work? Is it positive or
negative?
What motivates them most of all?
What information do they want from you?
How do they want to receive information from you? What is the best way of communicating
your message to them?
What is their current opinion of your work? Is it based on good information?
Who influences their opinions generally, and who influences their opinion of you? Do some of
these influencers therefore become important stakeholders in their own right?
If they are not likely to be positive, what will win them around to support your project?
If you don't think you will be able to win them around, how will you manage their opposition?
Who else might be influenced by their opinions? Do these people become stakeholders in their
own right?
A very good way of answering these questions is to talk to your stakeholders directly – people are often
quite open about their views, and asking people's opinions is often the first step in building a successful
relationship with them.
You can summarize the understanding you have gained on the stakeholder map, so that you can easily
see which stakeholders are expected to be blockers or critics, and which stakeholders are likely to be
advocates and supporters or your project. A good way of doing this is by color coding: showing
advocates and supporters in green, blockers and critics in red, and others who are neutral in orange.
In the example above, you can see that a lot of effort needs to be put into persuading Piers and Michael
of the benefits of the project – Janet and Amanda also need to managed well as powerful supporters.
You can create your own example of stakeholder analysis at work – whether for your current role, a job
you want to do or a new project. Conduct a full stakeholder analysis. Ask yourself whether you are
communicating as effectively as you should be with your stakeholders. What actions can you take to get
more from your supporters or win over your critics?
Key Points:
As the work you do and the projects you run become more important, you will affect more and more
people. Some of these people have the power to undermine your projects and your position. Others
may be strong supporters of your work. Stakeholder Management is the process by which you identify
your key stakeholders and win their support. Stakeholder Analysis is the first stage of this, where you
identify and start to understand your most important stakeholders.
The first stage of this is brainstorm who your stakeholders are. The next step is to prioritize them by
power and interest, and to plot this on a Power/Interest grid. The final stage is to get an understanding
of what motivates your stakeholders and how you need to win them around.