Fillable Printable Bristol Stool Color Chart
Fillable Printable Bristol Stool Color Chart

Bristol Stool Color Chart
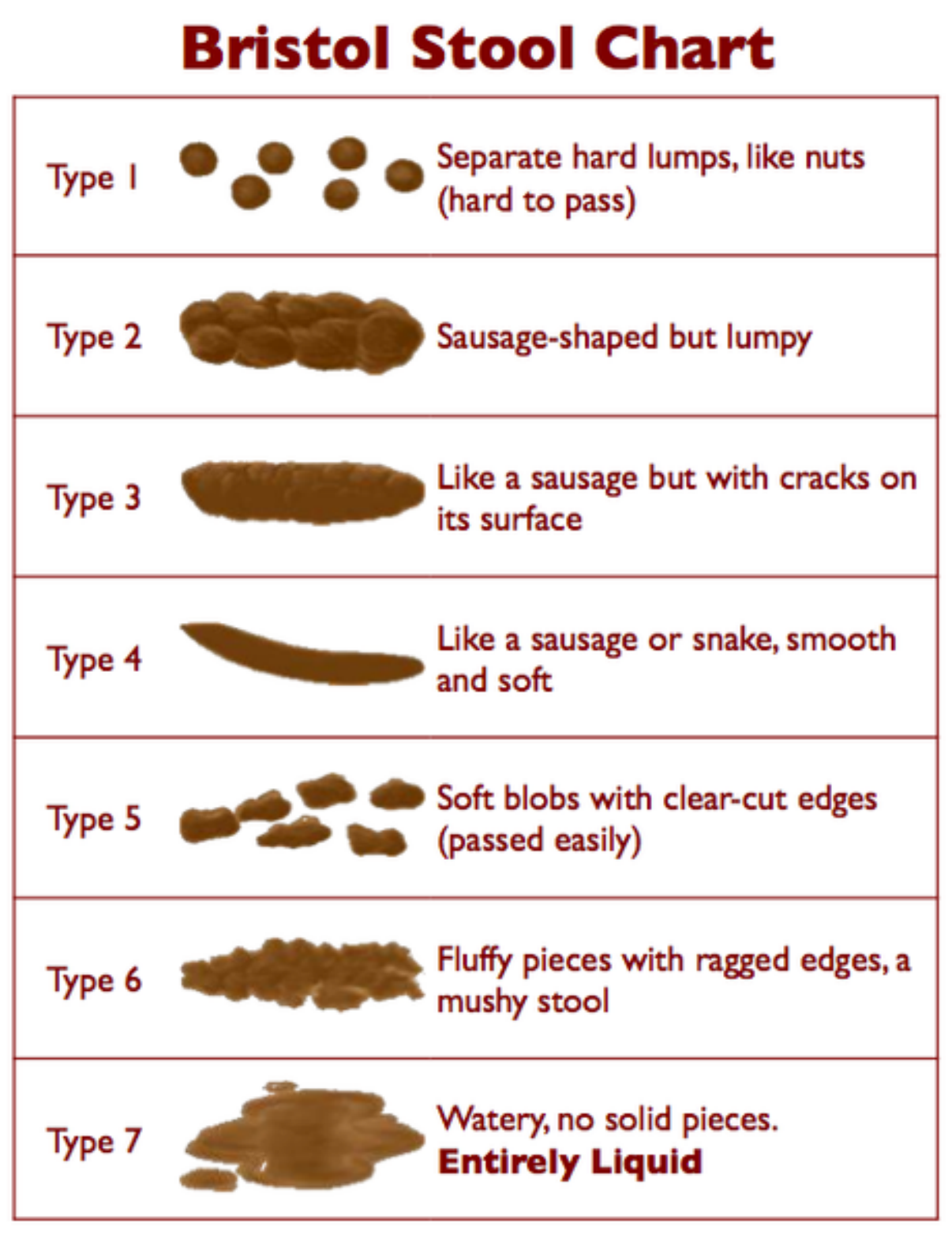
Type 1 has spent the longest time in the colon and type 7 has spent the least. Stools at the lumpy end of
the scale are hard to pass and often require a lot of straining. Stools at the loose or liquid end of the
spectrum can be too easy to pass - the need to pass them is urgent and accidents can happen. The ideal
stools are types 3 and 4, especially type 4, as they are most likely to glide out without any fuss.
What type of stools are best?
* The feeling you need to go is definite but not irresistible
* Once you sit down on the toilet there is no delay
* No conscious effort or straining is needed
* The stool glides out smoothly and comfortably
* Afterwards there is only a pleasant feeling of relief
* All this is most likely if the stool is Bristol Stool Form Scale, type 4
» Type 1: Separate hard lumps, like nuts
Typical for acute disbacteriosis. These stools lack a normal amorphous quality, because bacteria are
missing and there is nothing to retain water. The lumps are hard and abrasive, the typical diameter ranges
from 1 to 2 cm (0.4–0.8”), and they’re painful to pass, because the lumps are hard and scratchy. There is
a high likelihood of anorectal bleeding from mechanical laceration of the anal canal. Typical for post-
antibiotic treatments and for people attempting fiber-free (low-carb) diets. Flatulence isn’t likely, because
fermentation of fiber isn’t taking place.
» Type 2: Sausage-like but lumpy
Represents a combination of Type 1 stools impacted into a single mass and lumped together by fiber
components and some bacteria. Typical for organic constipation. The diameter is 3 to 4 cm (1.2–1.6”). This
type is the most destructive by far because its size is near or exceeds the maximum opening of the anal
canal’s aperture (3.5 cm). It’s bound to cause extreme straining during elimination, and most likely to
cause anal canal laceration, hemorrhoidal prolapse, or diverticulosis. To attain this form, the stools must be
in the colon for at least several weeks instead of the normal 72 hours. Anorectal pain, hemorrhoidal
disease, anal fissures, withholding or delaying of defecation, and a history of chronic constipation are the
most likely causes. Minor flatulence is probable. A person experiencing these stools is most likely to suffer
from irritable bowel syndrome because of continuous pressure of large stools on the intestinal walls. The
possibility of obstruction of the small intestine is high, because the large intestine is filled to capacity with
stools. Adding supplemental fiber to expel these stools is dangerous, because the expanded fiber has no
place to go, and may cause hernia, obstruction, or perforation of the small and large intestine alike.
» Type 3: Like a sausage but with cracks in the surface
This form has all of the characteristics of Type 2 stools, but the transit time is faster, between one and two
weeks. Typical for latent constipation. The diameter is 2 to 3.5 cm (0.8–1.4”). Irritable bowel syndrome is
likely. Flatulence is minor, because of disbacteriosis. The fact that it hasn’t became as enlarged as Type 2
suggests that the defecations are regular. Straining is required. All of the adverse effects typical for Type 2
stools are likely for type 3, especially the rapid deterioration of hemorrhoidal disease.
» Type 4: Like a sausage or snake, smooth and soft
This form is normal for someone defecating once daily. The diameter is 1 to 2 cm (0.4–0.8”). The larger
diameter suggests a longer transit time or a large amount of dietary fiber in the diet.
» Type 5: Soft blobs with clear-cut edges
I consider this form ideal. It is typical for a person who has stools twice or three times daily, after major
meals. The diameter is 1 to 1.5 cm (0.4–0.6”).
» Type 6: Fluffy pieces with ragged edges, a mushy stool
This form is close to the margins of comfort in several respects. First, it may be difficult to control the urge,
especially when you don’t have immediate access to a bathroom. Second, it is a rather messy affair to
manage with toilet paper alone, unless you have access to a flexible shower or bidet. Otherwise, I consider
it borderline normal. These kind of stools may suggest a slightly hyperactive colon (fast motility), excess
dietary potassium, or sudden dehydration or spike in blood pressure related to stress (both cause the rapid
release of water and potassium from blood plasma into the intestinal cavity). It can also indicate a
hypersensitive personality prone to stress, too many spices, drinking water with a high mineral content, or
the use of osmotic (mineral salts) laxatives.
» Type 7: Watery, no solid pieces
This, of course, is diarrhea, a subject outside the scope of this chapter with just one important and notable
exception—so-called paradoxical diarrhea. It’s typical for people (especially young children and infirm or
convalescing adults) affected by fecal impaction—a condition that follows or accompanies type 1 stools.
During paradoxical diarrhea the liquid contents of the small intestine (up to 1.5–2 liters/quarts daily) have
no place to go but down, because the large intestine is stuffed with impacted stools throughout its entire
length. Some water gets absorbed, the rest accumulates in the rectum. The reason this type of diarrhea is
called paradoxical is not because its nature isn’t known or understood, but because being severely
constipated and experiencing diarrhea all at once, is, indeed, a paradoxical situation. Unfortunately, it’s all
too common.