Fillable Printable Benefit Cost Analysis
Fillable Printable Benefit Cost Analysis
Benefit Cost Analysis
M M U
C o s t B e n e f i t A n a l y s i s t o o l k i t ( v 2 )
Page
1
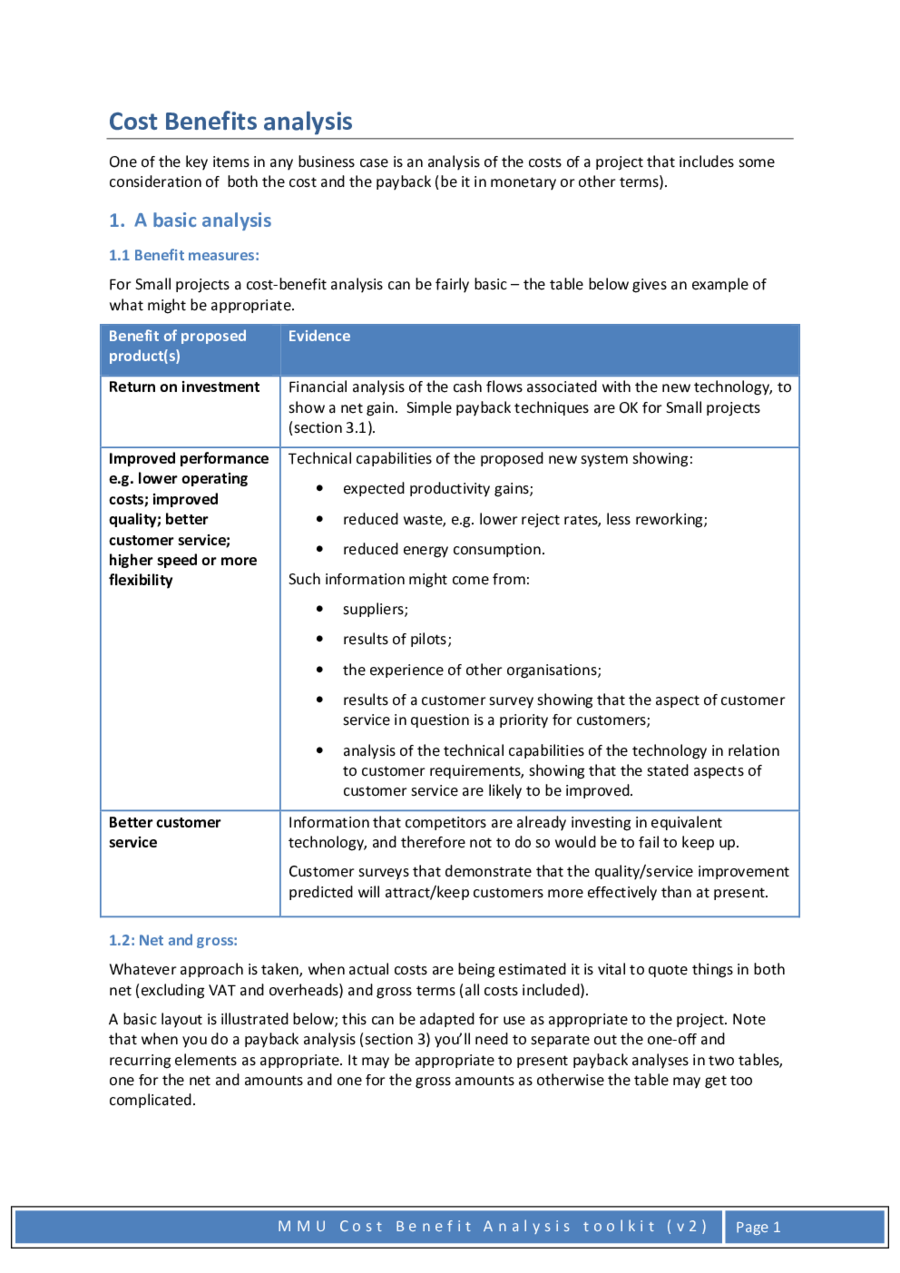
Cost Benefits analysis
One of the key items in any business case is an analysis of the costs of a project that includes some
consideration of both the cost and the payback (be it in monetary or other terms).
1. A basic analysis
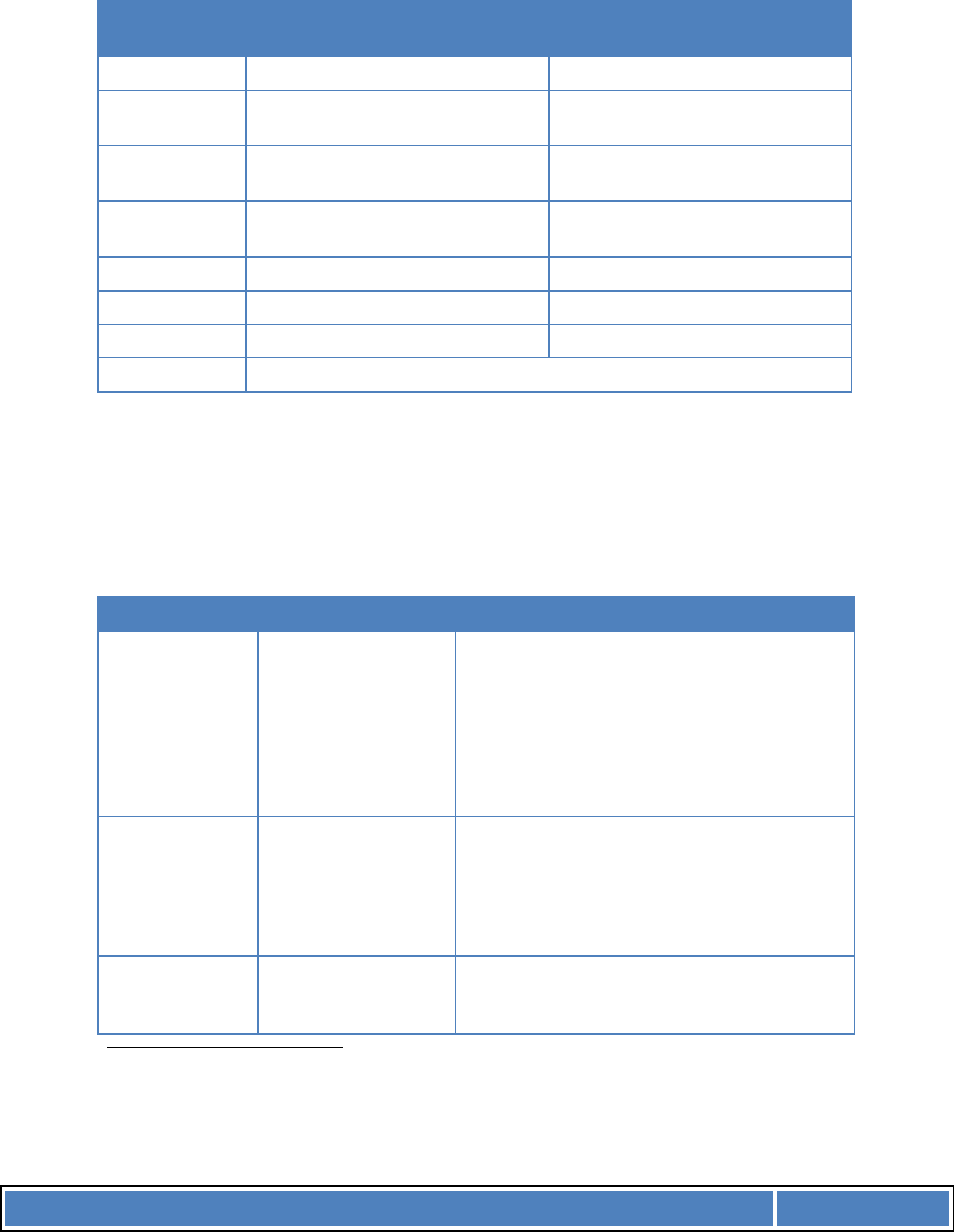
1.1 Benefit measures:
For Small projects a cost-benefit analysis can be fairly basic – the table below gives an example of
what might be appropriate.
Benefit of
proposed
product(s)
Evidence
Return on investment
Financial analysis of the cash flows associated with the new technolo
gy, to
show a net gain. Simple payback techniques are OK for Small projects
(section 3.1).
Improved performance
e.g. lower operating
costs; improved
quality; better
customer service;
higher speed or more
flexibility
Technical capabilities of the propose
d new system showing
:
• expected productivity gains;
• reduced waste, e.g. lower reject rates, less reworking;
• reduced energy consumption.
Such information might come from:
• suppliers;
• results of pilots;
• the experience of other organisations;
• results of a customer survey showing that the aspect of customer
service in question is a priority for customers;
• analysis of the technical capabilities of the technology in relation
to customer requirements, showing that the stated aspects of
customer service are likely to be improved.
Better
customer
service
Information that
competitors are already investing in equivalent
technology, and therefore not to do so would be to fail to keep up.
Customer surveys that demonstrate that the quality/service improvement
predicted will attract/keep customers more effectively than at present.
1.2: Net and gross:
Whatever approach is taken, when actual costs are being estimated it is vital to quote things in both
net (excluding VAT and overheads) and gross terms (all costs included).
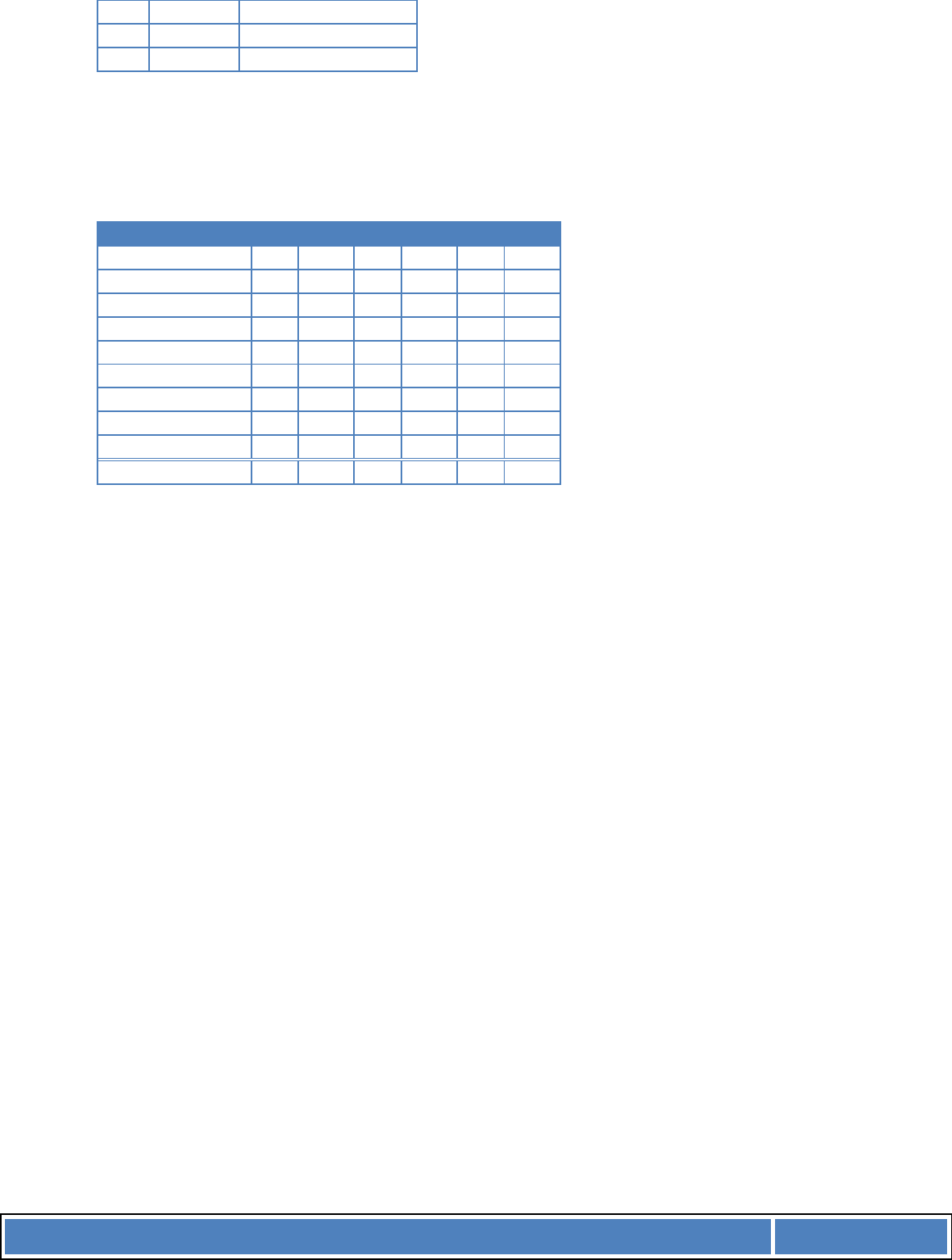
A basic layout is illustrated below; this can be adapted for use as appropriate to the project. Note
that when you do a payback analysis (section 3) you’ll need to separate out the one-off and
recurring elements as appropriate. It may be appropriate to present payback analyses in two tables,
one for the net and amounts and one for the gross amounts as otherwise the table may get too
complicated.
M M U
C o s t B e n e f i t A n a l y s i s t o o l k i t ( v 2 )
Page
2
Item
1
Net expenditure
(£)
Gross
expenditure
2
(£)
Net staff costs (£)
Gross staff costs
(£)
Item 1 purchase
10,000.00
12,000
.00
Item 1 annual
maintenance
3
1,250.00
1,500
.00
External
consultant
12,500.00
15,000.00
New staff
requirement
4
35,000.00
42,000
.00
Training
1,750.00
2,100
.00
Instal
lation
900.00
1080
.00
Totals
13,900
.00
16,680
.00
47,500
.00
57,000
.00
Grand total
73,680
.00
(gross)
2. A more comprehensive approach
2.1 Types of cost:
For Medium and Major Projects, there should be a greater amount of detail on costs and financial
analysis. The table below illustrates the main headings under which costs should be presented.
These are examples – it’s not an exhaustive list!
Financials
Consist of:
Options:
Income
Number of Admissions,
Research Grants
•
Sell higher priced items (overseas students)
• Increase convenience
• Improve service experience
• Improve quality/appeal
• Increase capacity
• Increase awareness
• Improve accommodation
• Do more courses
Produc
tion Cost
Courses,
Consumable facilities,
Media
•
Sell more lower-cost courses
• Increase course numbers
• Reduce course development costs
• Reduce course life costs
• Increase cross utilisation of resources
• Reduce waste
Labour Cost
(could split into
academic / non-
Wages,
Hours,
Output
•
Improve scheduling based on demand
• Improve training outcomes
• Foster teamwork
1
Line item – in enough detail that GL code can be assigned
2
Always state rate at which VAT is calculated – in this example it’s 20%
3
Always include recurring cost items and make it clear what the recurring cycle is, e.g. monthly, annually.
4
Always state staff overheads – in this example it’s 20%

M M U
C o s t B e n e f i t A n a l y s i s t o o l k i t ( v 2 )
Page
3
academic)
•
Reduce wages!
• Eliminate waste/improve work flow
• Improve attendance
Capital Costs
Land,
Facilities,
Construction
•
Reduce square footage requirements
• Buy cheaper real estate
• Reduce equipment/build out costs
• Reduce construction timeframes
2.2 Types of information:
There are various sources of information and you need to think about the balance between the
quality of the information (primary is usually better) versus the cost of getting it (secondary is usually
cheaper).
Primary
Secondary
Researched information (takes more time &
resource)
Existing information within then organisation
Internal:
• end-to-end measures of service;
• employee feedback;
• pilots/simulations.
Internal:
• costing information;
• internal reports;
• process & activity measures.
External:
• customer views;
• information about competitors;
• expert opinion.
External:
• market research reports;
• trade press & mass media;
• word of mouth/networks.
3. Some cost benefit analysis methods:
In the examples below, figures are presented without reference to net or gross amounts. In reality
you should always state both net and gross – see section 1.2
3.1 Payback:
This is literally the amount of time required for the cash inflows from a capital investment project to
equal the cash outflows.
Payback period = Initial payment / Annual cash inflow
So, if £4 million is invested with the aim of earning £500 000 per year (net cash earnings), the
payback period is calculated thus:
P = £4,000,000 / £500,000 = 8 years
Payback with uneven cash flows:
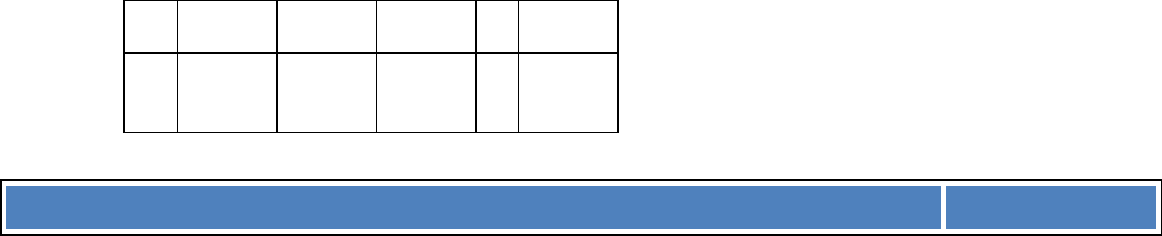
In the real world, investment projects by business organisations don't yield even cash flows. For
example (with an initial investment in year 0 of £4,000,000):
Year
Cash
flow
(£ 000)
Cumulative cash flow
(£ 000)
0
(4000)
(4000)
1
750
(3250)
2
750
(2500)
3
900
(1600)
M M U
C o s t B e n e f i t A n a l y s i s t o o l k i t ( v 2 )
Page
4
4
1000
(600)
5
600
Zero
6
400
400
The payback period is precisely 5 years.
The shorter the payback period, the better the investment, under the payback method. The main
issue with this is that, even for a short period, there is a sacrifice to be made: an up front investment
with the hope that it will be “paid back” in the future (also called opportunity cost).
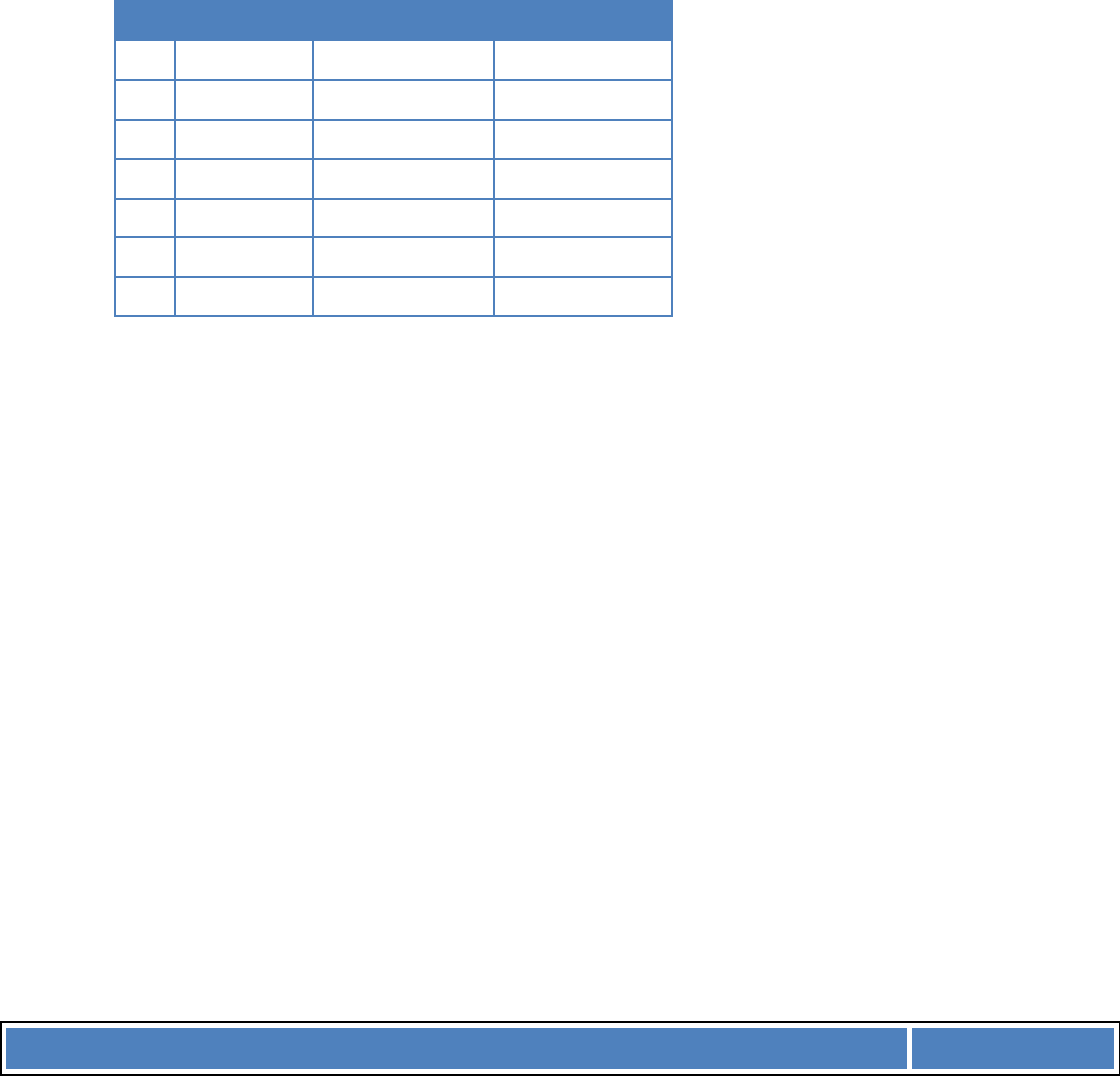
Another problem is when you are comparing several proposals, for example:
Project
Year
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
(50)
(100)
(80)
(100)
(8
0)
(100)
1
5
50
40
40
30
5
2
10
30
20
3
5
30
25
3
15
20
20
2
0
2
0
3
0
4
20
10
20
2
0
10
3
0
5
5
20
1
0
5
1
0
40
6
10
1
0
10
40
5
0
Payback period
4
3
3
4
3
5
Total after 6
years
5
40
40
30
60
80
The payback period for three of the projects (2, 3 and 5) is three years, so they seem to be of equal
merit.
However, because there is a time value constraint here, the four projects cannot be viewed as
equivalent. Project 2 is better than 3 because the revenues flow quicker in years one and two.
Project 2 is also better than Project 5 because of the earlier flows and because the post-payback
revenues are concentrated in the earlier part of that period. When you look at a longer time period,
the picture changes again: after 6 years projects 5 and 6 have the best yields, but although project 6
has the best overall yield, you have to wait the longest to get it.
Arguments in favour of payback
• It is simple! Research has shown that UK firms favour it. This is understandable given how
easy it is to calculate.
• In an environment of rapid technological change, systems may need to be replaced sooner
than in the past, so a quick payback on investment is essential.
Arguments against payback
• It lacks objectivity. It is decided by pitting one investment opportunity against another.
• Cash flows are regarded as either pre-payback or post-payback, but the latter tend to be
ignored.
• Payback takes no account of the effect on business. Its sole concern is cash flow.
Payback summary
It is best used as an initial screening tool, but it is inappropriate as a basis for sophisticated
investment decisions. In MMU it is OK for projects with budgets of up to £1 million. Projects with
greater costs should employ a more sophisticated analysis based on net present value (NPV) or
internal rate of return (IRR), as explained below.
M M U
C o s t B e n e f i t A n a l y s i s t o o l k i t ( v 2 )
Page
5
3.2 Average Rate of Return:
The average rate of return expresses the profits arising from a project as a percentage of the initial
capital cost. However the definition of profits and capital cost vary. For instance, the profits may be
taken to include depreciation, or they may not. One of the most common approaches is as follows:
ARR = (Average annual revenue / Initial capital costs) * 100
For example, a new system will cost £240,000 and is expected to generate total savings of £45,000
over the project's five year life.
ARR = (£45,000 / 5) / 240,000 * 100
= 3.75%
Arguments in favour of ARR
• As with the Payback method, the main advantage with ARR is its simplicity.
• There is also a link with some accounting measures that are commonly used. ARR is similar
to the Return on Capital.
• The ARR is expressed in percentage terms and this, again, may make it easier for managers
to use.
Arguments against ARR
• ARR doesn't take account of the project duration or the timing of cash flows over the course
of the project.
• The concept of savings (or profit) can be very subjective, varying with specific accounting
practice and the capitalisation of project costs. As a result, the ARR calculation for identical
projects could result in different outcomes from business to business.
• Thirdly, there is no definitive signal given by the ARR to help managers decide whether or
not to invest. This lack of a guide for decision making means that investment decisions
remain subjective.
3.3 Net Present Value:
The Net Present Value (NPV) is a Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) technique. It relies on the concept of
opportunity cost to place a value on cash inflows arising from capital investment.
Opportunity cost is the calculation of what is sacrificed or foregone as a result of a particular
decision. It is also referred to as the 'real' cost of taking some action.
Present value is the cash equivalent now of a sum receivable at a later date. If we didn’t spend that
money and banked it instead, the opportunity cost includes both the initial sum and the interest
earned.
NPV is a technique where cash inflows expected in future years are discounted back to their present
value. This is calculated by using a discount rate equivalent to the interest that would have been
received on the sums, had the inflows been saved.
Net Present Value Tables
Net Present Value tables provide a value for a range of years and discount rates:
0
1
2
3
-
-
-
n
Now
1 year
from now
2 years
from now
3 years
from now
n years
from now
M M U
C o s t B e n e f i t A n a l y s i s t o o l k i t ( v 2 )
Page
6
The present value for 0 years is always 1, and this is not included in the present value table.
If you are looking to find the present value of £ 150,000 which you expect to receive in 5 years time,
at a rate of interest of 3%, the following steps are taken:
• Step 1 Use a NVP lookup table (see separate spreadsheet: net_pres_value.xlsx) and find the
relevant number of years (5 years in this example).
• Step 2 Look across the row for relevant the rate of interest (3% in this example).
• Step 3 Take the value you have found from steps 1 and 2 (in this case this is 0.863 and
multiply the present amount (£150,000) = £129,450.
NPV Illustration
On its own, this doesn’t tell us much, so you’d then use this against your projected cash flows or
savings/profits, e.g.
Year
Cash Flow (£)
3%
Discount Rate
Present Value (£)
0
(
150,000
)
1.000
(
150,000
)
1
12,
000
0.971
1
1,652
2
25,
000
0.943
23,575
3
25,
000
0.915
22,875
4
35,
000
0.888
31,080
5
40,
000
0.863
34,520
Net Present Value
26,298
A positive NPV means that the project is worthwhile because the cost of tying up capital is
compensated for by the cash inflows that result. When more than one project is being appraised,
you choose the one that produces the highest NPV.
3.4 Internal Rate of Return (IRR):
Sometimes we will want to know how well a project will perform under a range of interest rate
scenarios. The aim with IRR is to answer the question: “What level of interest will this project be able
to withstand?” Once we know this, the risk of changing interest rate conditions can effectively be
minimised (especially in the current climate!).
The IRR is the annual percentage return achieved by a project, at which the sum of the discounted
cash inflows over the life of the project is equal to the sum of the capital invested.
Another way of looking at this is that the IRR is the rate of interest that reduces the NPV to zero.
Imagine a scenario where we are considering whether to accept or reject an investment project, on
the basis of their acquiring the funds necessary at a known rate of interest.
•
The NPV approach asks if the present value of cash inflows less the initial investment is
positive, at the current borrowing rate.
•
The IRR approach asks if the IRR on the project is greater than the borrowing rate.
Illustration of NPV & IRR
For example, using the above NPV illustration of a £150,000 project yielding a NVP of £26,298
we
know that the project seems worthwhile (positive result)

M M U
C o s t B e n e f i t A n a l y s i s t o o l k i t ( v 2 )
Page
7
Now, using IRR, we assume the 3% discount rate might well increase in the future so here’s the same
project using a 5% rate:
Year
Cash Flow (£)
5% Discount Rate
Present Value
(£)
0
-
15
0,000
1.000
-
150,000
1
12,000
0.952
11,429
2
25,000
0.907
22,676
3
25,000
0.864
21,596
4
35,000
0.823
28,795
5
40,000
0.784
31,341
Net Present Value
-
34,164
The negative result shows that 5% will be too high a rate, and the IIR will be somewhere between 3%
and 5%.
IRR = 3
% + Difference between the two discount rates *
Positive NPV
Range of
+
/ve to
-
/ve NPVs
IRR = 3% + (2
% *
26298
)
60462
IRR = 3.87%
IRR Summary
The value to a business of calculating the IRR is that its decision-makers are able to see the level of
interest that a project can withstand. In the case where a number of projects are competing for
selection, the one that is most resilient can be chosen.
IRR should not be used to compare mutually exclusive projects, however. For example a project with
a lower IRR may in fact have a higher NPV so the potential income (or saving) could be higher.
Also IRR should not be used to compare project of different durations because it doesn’t consider
cost of capital (expected return on capital).
Another problem with IRR appears with projects that have irregular cash flows alternating between
positive and negative values several times. Numerous IRRs can be identified for such projects
potentially leading to confusion and the wrong investment decisions being made.
3.5 Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR)
This is usually used to rank various choices. As the name implies, MIRR is a modification of the
Internal Rate of Return (IRR). MIRR adds up the negative cash flows after discounting them to time
zero, adds up the positive cash flows after factoring in the proceeds of reinvestment at the final time
period, then works out what rate of return would equate the discounted negative cash flows at time
zero to the future value of the positive cash flows at the final time period. This rate of return is the
MIRR.
Luckily there is an Excel formula to calculate MIRR which takes three arguments: the range of values
of payments / income over the period of the project, the interest rate, and the reinvestment interest
rate. Here’s a worked example using the £150,000 project and the same cash flow as in the above
example:

M M U
C o s t B e n e f i t A n a l y s i s t o o l k i t ( v 2 )
Page
8
Data
Description
-
150
,
000
Initial cost
12,000
Return first year
25,000
Return second year
25,000
Return third year
35,000
Return fourth y
ear
40,000
Return fifth year
3.0%
Annual interest rate for the
£
150,000 loan
2.0%
Annual interest rate for the reinvested profits (likely scenario)
5
.0%
Annual interest rate for the reinvested profits (hopeful scenario)
-
1
.2
%
Investment's MIRR after f
ive years (likely)
-
0
.3
%
Investment's MIRR after five years (hopeful)
In Excel, here’s what you would enter for the data column:
A
1
Data
2
-
150000
3
12000
4
25000
5
25000
6
35000
7
40000
8
3.0%
9
2.0%
10
5.0%
11
=MIRR(A2:A7, A8,A9)
12
=MIRR
(A2:A7, A8, A10)
You can, of course, do “what-if” scenarios by varying the percentage amounts in cells A8, A9 and
A10, or by giving different values for the return for each year. According to our current example, this
would be quite a risky project in terms of cash return (though of course there may be other reasons
why we want to do it).
Bruce Levitan
Business Improvement Manager
October 2010 (v2)