Fillable Printable Cost Estimating Guide for Infrastructure Construction
Fillable Printable Cost Estimating Guide for Infrastructure Construction

Cost Estimating Guide for Infrastructure Construction
Cost Estimating Guide
1-Overview
Last R ev ised: 12/13/2012
Page 1 of 2
1.Overview
Follow this guide when preparing cost estimates for all infrastructure projects. It is
applicable to all infrastructure projects, including habitat and other "green" infrastructure
projects, pipeline, storage, and other "gray" infrastructure pr ojects.
Cost estimates prepared using this guide are usedfor the following purposes:
helps with portfolio management and project prioritization
developing proposed rates
develop SPU’s 6-year Capital Improvement Program (CIP)
developing the CIP budget submittal
evaluating options and making stage gate, value engineering, and other business
decisions
use in contract advertisements
manage costs and ensure projects are completed within approved funding levels
communicate project costs to internal and external stakeholders.
This guide provides templates and directions for preparing project cost estimates. You
may need to supplement the guide with professional construction cost estimating
expertise to develop high quality project estimates, especially on l a rge or co m p lex
projects. If you can’t find the answers to your cost estimating questions in this guide,
please contact the Cost Estimating Guide support team atSPU_CEG@seattle.gov
.
For small projects, the “Small Project Management Plan” included in the“Small Project
Guidance” section of the Project Management Methodology
may be used instead of the
templates in the Cost Estimating Guide. The fundamental concepts of the guide are still
valid for small projects.
1.1.Frequency of Cost Estimate Updates
Cost estimates typically are prepared and/or updated at the following times :
During Initiation, to obtain Stage Gate 1 approval;
During Options Analysis, as part of the Stage Gate 2 business case;
Immediately following Stage Gate 2 approval, as part of developing the Project
Management Plan (PMP);
At 30% Design;
At 60% Design;
At 90% Design;
At Final Design, to obtain Stage Gate 3 approval;
Following bid opening, to obtain Stage Gate 4 approval; and
At regular intervals during Construction, including Closeout.
Unlike the initial estimate and other updates, the update prepared for the Stage Gate
2 business case includes estimates for each option
. The economic analysis in the
business case at Stage Gate 2 compares the present value of Triple Bottom Line life
cycle costs for all options.
In addition to the updates listed above, cost estimates are updated as part of SPU’s
change management process
and are reviewed monthly in the Enterprise Project
Management System (EPMS) and annually as part of SPU's budget and spending plan
development processes.

Cost Estimating Guide
1-Overview
Last R ev ised: 12/13/2012
Page 2 of 2
1.2.Cost Estimate Guide Diagrams
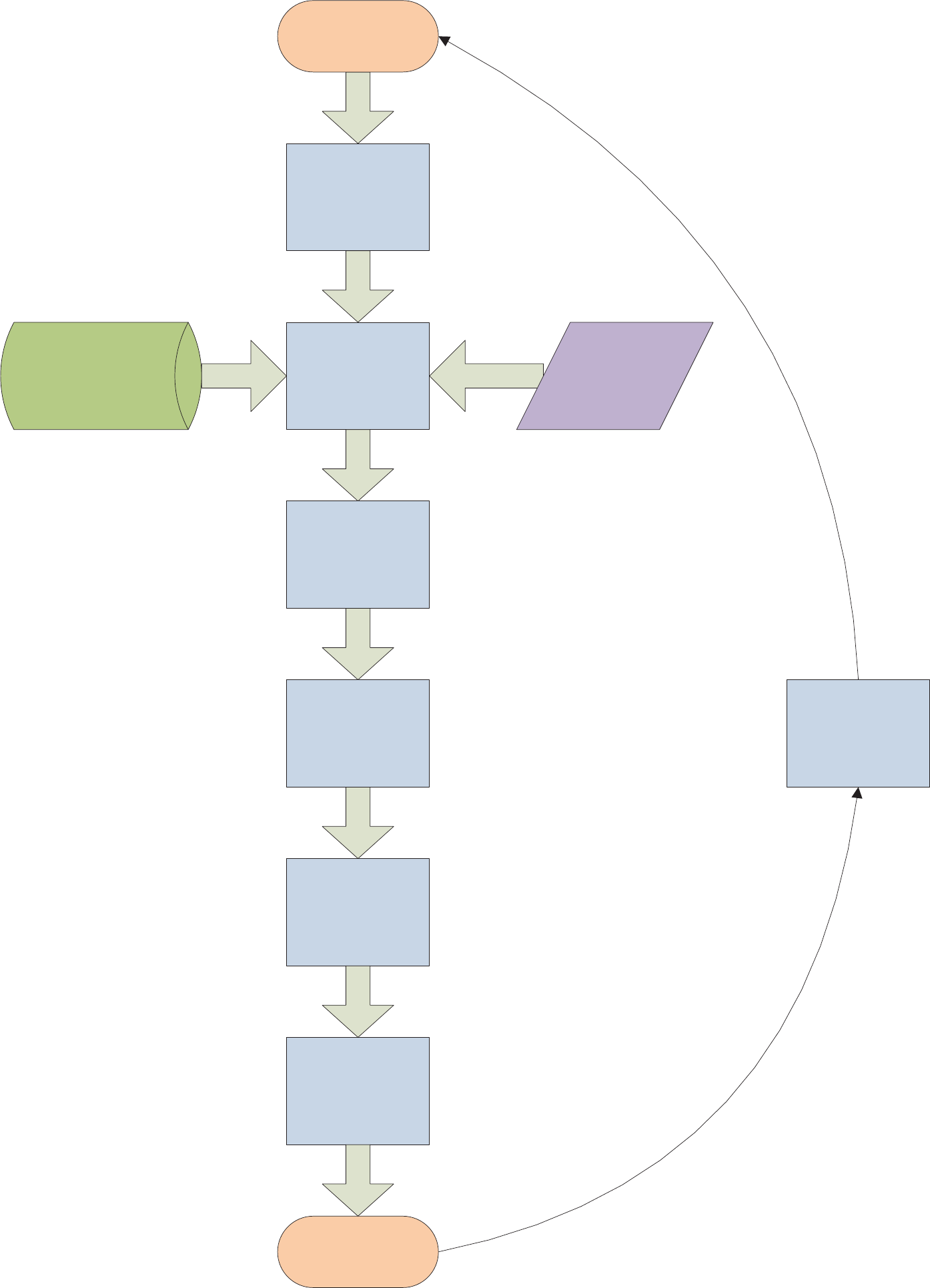
Figure 1-1 shows the step-by-step process used to develop and update cost
estimates. The remainder of this guide follows the order of these steps and provides
directions for each step. Each time you update a project cost estimate, you need to
update the Basis of Estimate and each Basis of Estimate update needs to describe
what’s changed.
Figure 1-2
shows the estimate components andhow these components are
aggregated.
Figure 1-3
shows cost estimate attributes and uses by project phase, including who is
responsibl e for preparing estimates and updates, the expected approach and level of
detail, the level of uncertainty at var ious times in the project delivery cycle, and the
decision-making processes where cost estimates are used, including stage gates,
rates and budge ting, and value e ngineering.
Figure 1-4
shows the methods used in each phase to estimate the main cost estimate
components. The figure also shows how, as a project prog resses through its phases,
uncertainty decreases with successive updates of the cost estimate. As design details
are developed, unknowns become known, the allowance for indeterminates
decreases, id entified risk events are pass ed, more rigorous estimating methods are
used, actual project costs are incurred, the uncertainty in the estimated remaining
project costs decreases, and the project reserves decrease.
Estimatethe
BaseCost
(Section3)
SimilarCompleted
Projects/Historical
CostInformation
Subject
Matter
Experts
ProjectScope/
ProjectSchedule
Establishthe
Project
Reserves
(Section4)
Developthe
TotalCostand
TotalCost
Projection
(Section5)
Reviewthe
CostEstimate
(Section6)
Communicate
theCost
Estimate
(Section7)
CostEstimate
Updatethe
CostEstimate
Documentthe
Basisof
Estimate
(Section2)
Figure 1-1:
Cost Estimating Process
Cost Estimating Guide
Figure 1-2: Cost Estimate Components
Fig ure 1-2 (Cost Estimate
Components)
Last R ev ised: 10/20/2011
Page 1 of 1
Inflation
TOTAL COST PROJECTION (all costs escalated to year of projected spending)
Reserves
Management Reserve
TOTAL COST ( expressed in today’s dollars )
Contingency Reserve
Propert y Acquisition Costs
BASE COST
Soft Cost
Soft Costs
Hard Costs
Crew Construction Costs
CONSTRUCT I ON COST
Miscellaneous Hard Costs
Sales Tax
CONSTRUCT ION CONTRACT AMO UNT
Known Market Conditions
CONSTRUCT I ON BI D AMOUNT
Allowance for Indeterminates
Construction Line Item Pricing
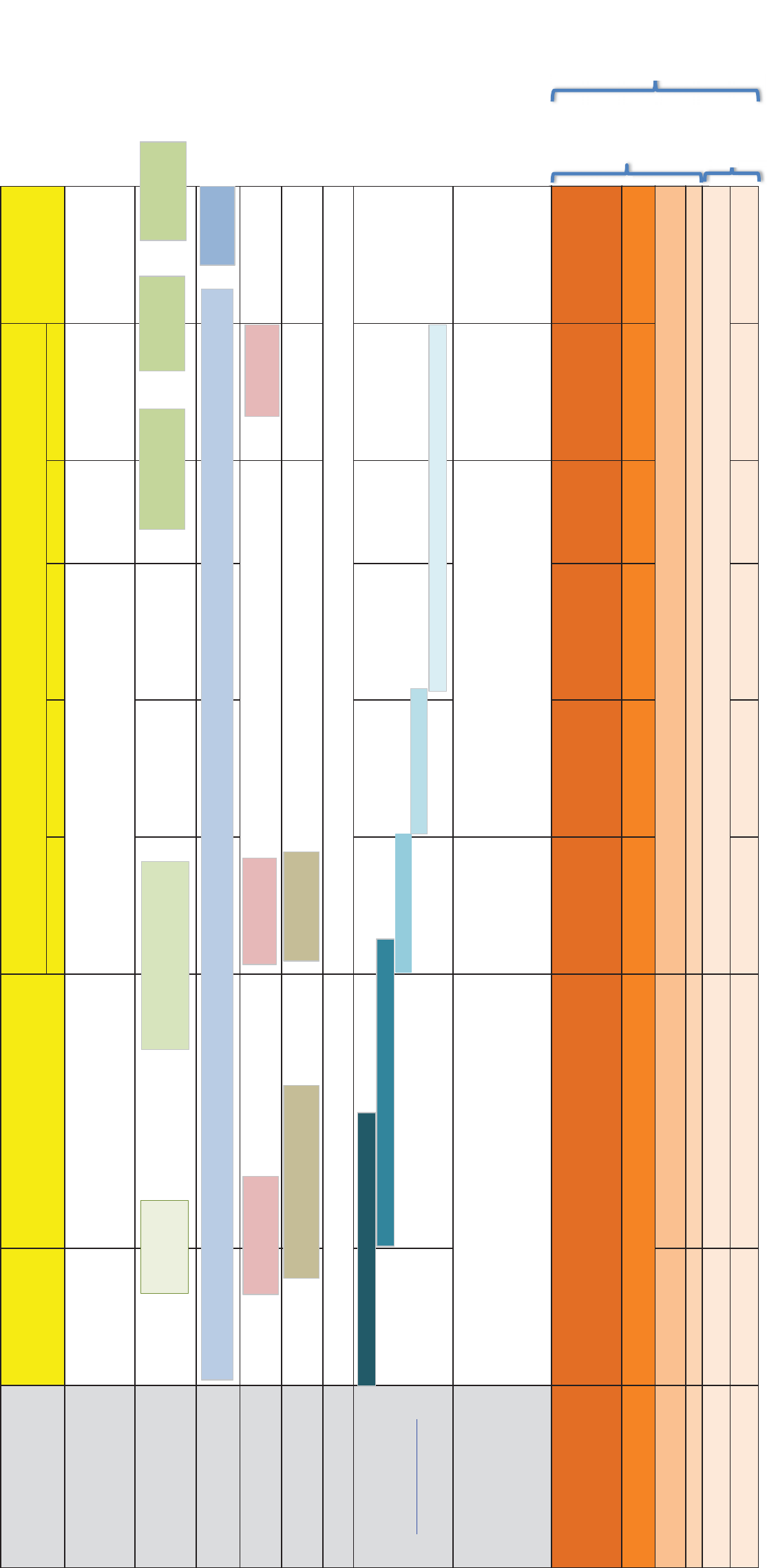
Figure 1-3: Cost Estimate Attributes and Uses by Project Phase
30%60%90%FinalBid
Comprehensive Planning
Portfolio Prioritization
Project Identification
Financial Planning
Ensure funding
Publish to inform bidders
and validate / review
contractor bid
Change orders and
contractor negotiations
Project Scope, Schedule.
CCBS for construction
cost and WBS for soft
cost. Vendor Quote,
industry data and
historical costs.
Apparent Low or Best
Value Bidder
Actual and Anticipated
Cost
Line Item Costs for Major
Items and Equipment
Line Item Costs for Major
Items and Equipment;
Semi-detailed Line Item
Unit Costs for Remainder
Line Item Costs for Major
Items and Equipment;
Increased Detailing of
Remainder
Detailed Take Off,
Unit Costs
Apparent Low or Best
Value Bidder
Including Change Orders
15% to 25% of Bid Cost5% to 15% of Bid Cost0% to 5% of Bid Cost0% of Bid CostN/AN/A
Include KC assessment if
site determined
Recent SPU Soft Costs
25% to 40% of Base Cost
10% to 25% of Base Cost 5% to 15% of Base Cost5% to 10% of Base Cost0% to 5% of Base Cost
0% to 5% of Base
Cost
0% to 5% of Base Cost0% to 5% of Base Cost
CIP - Capital Improvement Project, SOW - Scope of Work, CCBS - Construction Cost Breakdown Structure, WBS - Work Breakdown Structure, KC - King County, PMP - Project Management Plan,
Phase
InitiationOptions Analysis
Construction & Close
Out
Specifier
Project Manager
Basis of Estimate
Project Management Plan
Who's responsible for cost
estimate?
Value Analysis/ Value
Engineering
Contingency
Construction Bid Cost
Allowance for Indeterminates
Property/Permit Fees
Soft Cost
Historical Unit Costs, Costs of Similar Completed Projects, and/or Expert
Judgement
Included in Base Cost
Desktop Geotech, Property based on KC Assessor
and $/sq ft for Easements
Based on Appraisals and Site Conditions
Based on PMP and Consultants SOW
What activity is cost estimate
used or updated for?
Stage Gate/Funding Request
Rates and Budget
Project Management and Control
Feasibility Analysis/Select Preferred Option
Design
AACE Estimate Class
(see AACE for guidance
)
15% to 25% of Base cost
10% to 20% of Ba se Cost
Based on PMP Risk Register
Management Reserve
By Phase/Org, Based on Recent SPU Soft Costs
On Problem Statement/Project Objectives, Project Schedule. Construction
Costs Based on Historical Unit Costs, Costs of Similar Completed Projects,
and/or Expert Judgement. Soft Costs Based on SPU Recent Soft Costs.
Project Scope, Schedule. Preferred Design Solution. Construction
Costs based on CCBS and Soft Costs based on WBS
Class 5
Class 4
Class 3
Class 2
Class 1
Depreciation
Schedule
1. Approve
Funding for
Options Analysis
2. Approve Preferred Option, Funding
for Design, Placeholder for Total Cost
Projection and O&M
3. Approve Construction
Cost
4. Approve
Const. Contract
Cost
Estimate Used
to Set Baseline
Base
Cost
May Be Used for
Options Analysis
Total Cost
(in today's
dollars);
Total Cost
Projection
(all costs
escalated
to year of
projected
spending)
Reserves
5. Approve Project
Close Out & Asset
Costing
Estimate
Required for VA
Updated Estimate
Required for VE
Update Cost
Estimate in PMP
6 Yr. CIP Budget,
Annual Spending Plan
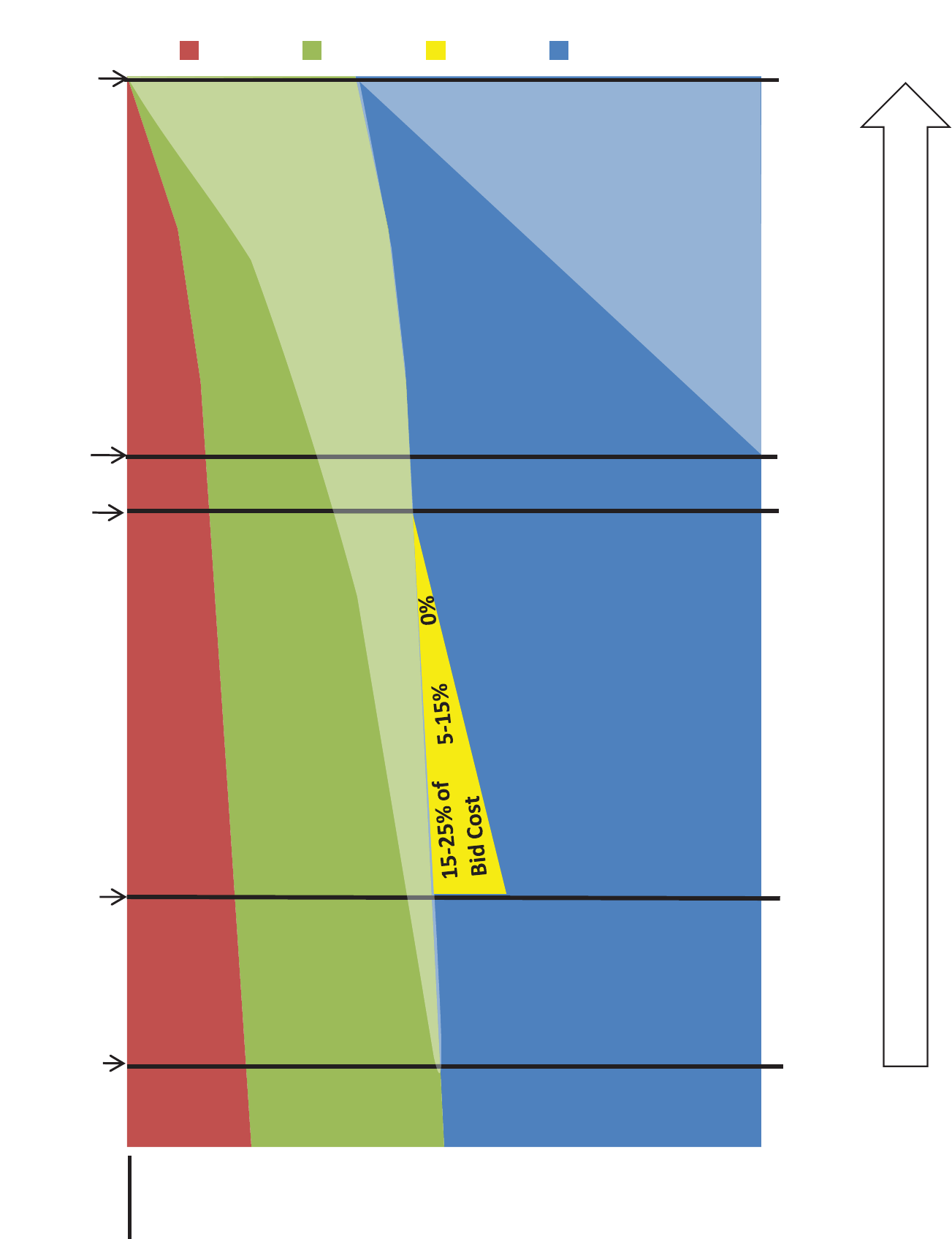
Total Project Cost
Project Reserves
Soft Costs
Allowance for
Indeterminates
Hard Costs
Semi-detailed,
Unit Costs,
Historic Costs,
Similar Projects
Detailed
Take-offs,
Unit Costs,
Appraisals &
Site
Conditions
Historic
Costs, Similar
Projects &
Judgement
Soft Cost
Table
WBS Detail by
Org/Phase as
Developed in
PMP
Stage
Gate
1
Stage
Gate
2
Stage
Gate
3
Stage
Gate 4
Stage
Gate
5
Risk-based,Probabilistic
Simulation
Judgement,
Historic,Similar
Project
Historic Costs, Similar Projects & Judgment
Cost Estimate Updates by Project Phase, Uncertainty Decreases
Actual
Life-to-date
Hard Cost
Expenditures
Actual Life-to-date
Soft Cost Expenditures
30% 60% 90% 100% Bid
InitiationOptionsDesignConstruction Closeout
Analysis

Cost Estimating Guide
2-Document the Basis of Estimate
Last R ev ised: 11/21/2011
Page 1 of 2
2.Document the Basis of Estimate
The Basis of Estimate summarizes the information, assumptions, and methodology
used to develop a project cost estimate. A well-pre pared Basis of Estimate helps people
develop, understand, use, and update a costestimate, and helps avoid estimating errors
and omissions. Each time you update an estimate, update the Basis of Estimate and
show what has changed. During the Options Analysis phase, complete one Basis of
Estimate template, noting any differences between the alter natives that are being
considered. If the options are substantially different, complete a separate Basis of
Estimate for each alternative.
The topics you’ll need to cover in a Basis of Estimate are listed below. Some may find it
easier to go directly to the template, which includes instructions:
Tools and Templates
Basis of Estimate Template
2.1.Determine the Appropriate Level of Detail
Use your best judgment to determine the appropriate level of detail in the Basis of
Estimate. Consider the project size and complexity, the type of project, the degree of
project definition (well-defined versus vague), and the number and type of estimate
assumptions. The Basis of Estimate should include enough detail to communicate key
assumptions, to enable an independent review of the estimate, and to provide a basis
for change management.
2.2.Complete the Basis of Estimate Template
You'll need to provide basic template information, including the project name, activity
number(s), line of business, estimate date, names and roles of the estimators, and
current project phase. A complete Basis of Estimate also includes the following
information:
Project Objecti ves
Project Scope
Project Location, including constraints and site issues
Project Schedule
Project Labor R esourci n g Strategy
Construction Contracting Strategy
Cost Estimating Methodology and Sources of Information
Allowances
Other Assump tions
Exceptions
Risks
Estimate Reviews
How and Why the Estimate Has Changed (with each update)
Benchmarking
Reference Documents

Cost Estimating Guide
2-Document the Basis of Estimate
Last R ev ised: 11/21/2011
Page 2 of 2
Before Stage Gate 2 you may not have some of this information, but after Stage Gate
2 all of these sections should be completed. You may find it helpful to keep an
estimate variance log to track how and why your estimate has changed.
Benchmarking is especially helpful on projects with high cost uncertainty and/or
significant changes in the overall estimate.
2.3.Where to Get Additional Information
Additional information on preparing a Basis of Estimate is available from the
Association for the Advancement of Cost Engineering (AACE), Recommended Practice
No. 34R-05, Cost Estimating and Budgeting - Basis of Estimate.

Basis of Estimate
Basis of Estimate Last Revised: 2/23/2012 Page 1 of 3
Provide the information described in red and then delete the red text.
Date Estimate Prepared <<enter date>>
Project Phase <<Initiation, Options Analysis, 30/60/90/Final>>
AACE Estimate Class <<Class 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5>>
1.Project Information
Project Name
Activity Number
Specifier
Project Manager
Cost Estimator(s)
Estimate Reviewer(s)
2.Objectives
Provide a concise description of the project purpose and objectives. This in formation should
match the “Problem/Opportunity, Key Drivers, and Objectives” section of the Stage Gate 2.
<<enter text here>>
3.Scope
Provide a brief description of the project scope of work, including the type of project (e.g.,
sewer rehab, water reservoir, etc.) and each major item of work. Note whether there are
any new or modified structures or structures that must be demolished and whether the
work will requ ire an y shut-downs or connections. Note that, for projects that have passed
Stage Gate 2, the project scope statement can be taken from the Project Management Plan.
<<enter text here>>
4.Location
Identify th e project location; any site constraints th at may affect access, mobilization, or
construction; and any significant site issues that must be addressed (e.g., wetlands,
hazardous materials, and/or archaeological impacts). Be sure to consider how the site has
been used historically, and identify any site contamination or other problems that may exist
as a result.
<<enter text here>>
5.Schedule
This information should match the “Schedule” section of the Stage Gate 2; after SG2, refer
to the Project Management Plan. Summarize the anticipated project schedule, or attach the
project schedule if there is a current version that includes anticipated stage gates, key
milestones and deadlines, and any construction windows or other schedule constraints.
Projects that have passed Stage Gate 2 should include increasingly detailed schedules.
<<enter text here>>

BasisofEstimate
Basis of Estimate Last Revised: 2/23/2012 Page 2 of 3
6.Labor Resourcing Strategy (optional for Stage Gate 1)
Identify what work will be performed by SPU and what work will be performed by
consultants, if any. For the work performed by SPU, identify what branch and division will
provide the resources. For the work to be performed by consultants, describe the approach
and schedule you will use to procure consultant services. Identify any field crew
construction resources that will be needed. Describe any assumptions regarding workweek
schedule and overtime.
<<enter text here>>
7.Construction Contracting Strategy (optional for pre-Stage Gate 2)
Note the planned contracting approach (e.g., design-bid-build, General Contractor/
Construction Manager, design-build, job order contract). Summarize any construction
assumptions, work hour constraints and seasonal supply or construction constraints. Note if
SPU is providing materials or other scope items to the contractor.
<<enter text here>>
8.Cost Estimating Methodology and Sources of Information
For projects projects at Stage Gate 2 or before, the basis of estimate should detail
all assumptions that support the doll ar amounts associated with all Cost Items.
List the primary estimating methodology(ies) used for the construction cost estimate:
xHistorical unit costs ($/MG, $/SF, $/LF),
xSimilar completed project costs,
xProfessional cost estimating judgment,
xSemi-detailed unit costs,
xDetailed unit costs
List the primary estimating methodology(ies) used for the soft cost estimate:
xSPU Cost Estimating Guide Table 3.2 (through Stage Gate 2)
xEstimates from the Project Management Plan (following Stage Gate 2)
List the engineering deliverables used to prepare the construction cost estimate:
xDesign assumptions,
xConceptual drawings/plans (XX% design),
xSpecifications,
xEquipment lists
List the sources of information used in the estimate, in cluding:
xPricing sources for construction and consultant costs, such as ASCE Cost Curves,
SPU Unit Cost Report, RSMeans, King County’s Tabula planning tool estimator,
other projects, etc. and what these costs include (contract line items, an
Allowance for Indeterminates, sales tax, permit fees, construction phase survey
and materials testing, and/or crew construction costs)
xTax rates as applicable
xConstruction cost indices and/or market condition adjustments used to update
historical costs to estimates expressed in today’s dollars
xReal Property pricing source, if applicable

BasisofEstimate
Basis of Estimate Last Revised: 2/23/2012 Page 3 of 3
<<enter text here>>
9.Allowances
Identify any allowances included in the estimate and how they were determined, including
how the Allowance for Indeterminates (AFI) was determined.
<<enter text here>>
10.Other Assumptions
Identify any additional assumptions that may affect the cost estimate, including any
assumptions about work that will NOT n eed to be performed.
<<enter text here>>
11.Exceptions
Identify any variances to SPU’s cost estimating practices and any significant deviations from
the deliverables normally required for the current phase.
<<enter text here>>
12.Risks
This information should match the “Key Risks & Issues” section of the Stage Gate 2; after
SG2, refer to the Project Management Plan. Identify any part of the cost estimate having
significant risk. Provide a copy of the project Risk Register from the PMP Process if one has
been prepared. In particular, identify the cost and schedule elements that have high or
critical risk values.
<<enter text here>>
13.Estimate Reviews
Describe all estimate reviews to date and the results. Identify any additional planned
estimate reviews.
<<enter text here>>
14.How and Why the Estimate Has Changed
Summarize the differences between the original estimate and each update, so that the
reader understands how the estimate has changed and why. A detailed reconciliation or
cost trending report may be included as an additional attachment if necessary on large,
complex projects.
<<enter text here>>
15.Benchmarking
Describe any cost benchmarking performed with similar projects and the results. Explain
any significant differences in cost or efficiency.
<<enter text here>>
16.Attachments
Include any attachments referred to in the Basis of Estimate (e.g., project schedule).
<<enter text here>>