Fillable Printable Educational Software Evaluation Form
Fillable Printable Educational Software Evaluation Form
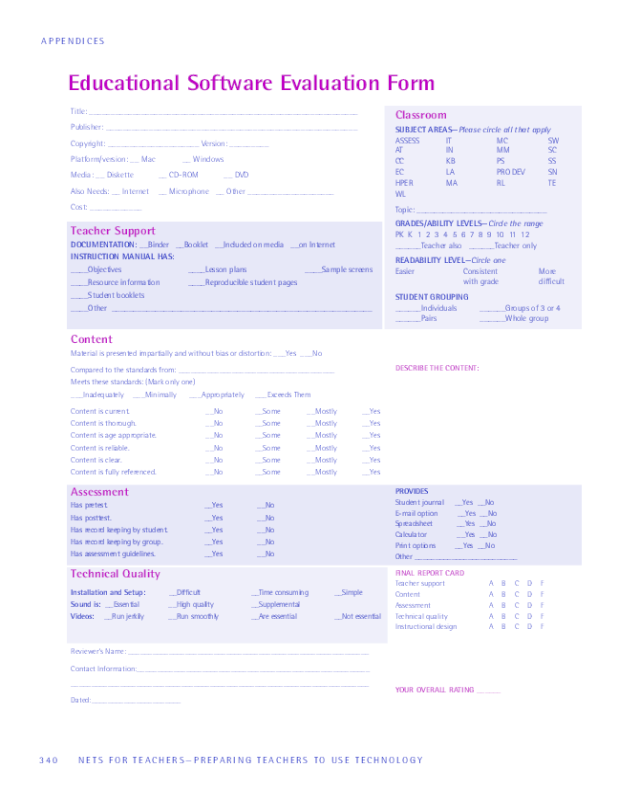
Educational Software Evaluation Form
340
NETS FOR TEACHERS— PREPARING TEACHERS TO USE TECHNOLOGY
APPENDICES
Reviewer’s Name: ___________________________________________________________
Contact Information:_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
Dated:______________________
Title: ______________________________________________________________
Publisher: __________________________________________________________
Copyright: _____________________ Version: _________
Platform/version: __ Mac __ Windows
Media: __ Diskette __ CD-ROM __ DVD
Also Needs: __ Internet __ Microphone __ Other ____________________
Cost: ____________
Teacher Support
DOCUMENTATION: __Binder __Booklet __Included on media __on Internet
INSTRUCTION MANUAL HAS:
____Objectives ____Lesson plans ____Sample screens
____Resource information ____Reproducible student pages
____Student booklets
____Other ____________________________________________________________
Content
Material is presented impartially and without bias or distortion: ___Yes ___No
Compared to the standards from: ______________________________________
Meets these standards: (Mark only one)
___Inadequately ___Minimally ___Appropriately ___Exceeds Them
Content is current. __No __Some __Mostly __Yes
Content is thorough. __No __Some __Mostly __Yes
Content is age appropriate. __No __Some __Mostly __Yes
Content is reliable. __No __Some __Mostly __Yes
Content is clear. __No __Some __Mostly __Yes
Content is fully referenced. __No __Some __Mostly __Yes
Assessment
Has pretest. __Yes __No
Has posttest. __Yes __No
Has record keeping by student. __Yes __No
Has record keeping by group. __Yes __No
Has assessment guidelines. __Yes __No
Technical Quality
Installation and Setup: __Difficult __Time consuming __Simple
Sound is: __Essential __High quality __Supplemental
Videos: __Run jerkily __Run smoothly __Are essential __Not essential
Classroom
SUBJECT AREAS—Please circle all that apply
ASSESS IT MC SW
AT IN MM SC
CC KB PS SS
EC LA PRO DEV SN
HPER MA RL TE
WL
Topic: ______________________________
GRADES/ABILITY LEVELS—Circle the range
PK K 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
______Teacher also ______Teacher only
READABILITY LEVEL—Circle one
Easier Consistent More
with grade difficult
STUDENT GROUPING
______Individuals ______Groups of 3 or 4
______Pairs ______Whole group
Educational Software Evaluation Form
DESCRIBE THE CONTENT:
FINAL REPORT CARD
Teacher support A B C D F
Content A B C D F
Assessment A B C D F
Technical quality A B C D F
Instructional design A B C D F
YOUR OVERALL RATING ______
PROVIDES
Student journal __Yes __No
E-mail option __Yes __No
Spreadsheet __Yes __No
Calculator __Yes __No
Print options __Yes __No
Other _________________________
NETS FOR TEACHERS— PREPARING TEACHERS TO USE TECHNOLOGY
341
APPENDIX D • EVALUATION FORMS
Instructional Design
CIRCLE THE MODES THAT APPLY
AC AU BL CA CP DE DP EG EX GP IN LEP MM PS RF SI TE TL TU
PROMOTES
___ Creativity ___ Collaboration ___ Discovery
___ Higher-order thinking ___ Problem solving ___ Memorization
MOTIVATIONAL
___ Student controls pacing ___Stimulates curiosity ___Challenging ___Real-world connections
STRENGTHS:
WEAKNESSES:
DESCRIBE THE LEARNING STRATEGY INCORPORATED IN THE DESIGN:
(Either here or on another page)
RECOMMENDATIONS:

342
NETS FOR TEACHERS— PREPARING TEACHERS TO USE TECHNOLOGY
APPENDICES
Using the Educational Software Evaluation Form
The goal of this form is to provide teachers with an evaluation guide that focuses on the educational use
of a technology resource. This form can be used for software, an Internet site, a laserdisc, or any other
technology-based resource to be used with students.
The abbreviations and classifications used throughout the form are consistent with those in the 2002
Educational Software Preview Guide published by ISTE.
This form is not the final word on evaluation. You are encouraged to modify the criteria so they address
your school’s or district’s needs. For example, cost is often crucial in determining whether a resource can
be recommended for purchase. So, in addition to a rating, you might add another category—
“Recommend for Purchase”—with grades or just a “yes/no” option.
USING THE FORM
1. Schedule enough time to examine materials, install any programs, explore the level of
interactivity, and set up any management components.
2. Write your name and contact information in the lower left of the form. This information is only
for the person collecting the information—someone who may need to clarify your comments—
not for general distribution. If this review is to be viewed in a public place, then the reviewer
box could contain only an identification code.
3. Use the publisher’s materials to supply the publisher, copyright, version, and cost. You may also
want to list the company’s Web site. Circle all the hardware platforms that apply to the resource
you are evaluating. List further needs under “Also needs,” for example, “at least 8 MB of RAM.”
4. Look through the documentation and note what is contained under the section titled “Teacher
Support.” Instead of checking any of the items listed there, you may want to insert a qualifier or
quantifier to indicate the quality of support material in the documentation. Many publishers
now include manuals on CD-ROM or at their Internet sites; record that information, too. If the
publisher provides documentation only in an electronic form, then reduce the grade for teacher
support. The documentation should have all the information needed to make any necessary
installations.
5. You might want to use pencil to fill in the “Classroom” section. Publishers may provide
information that accurately describes their materials in relation to subject area, topic, grade
level, readability, and special-needs provisions.
If you examine the material and still feel a different set of selections is more appropriate, then use your
ink pen. The subjects are:
ASSESS Assessment (Includes tests and testing)
AT Fine Arts, such as music, performing arts, and visual arts
CC Cross Curricular
EC Early Childhood
HPER Health/Physical Education/Recreation
IT Instructional Tools
IN Internet/World Wide Web
KB Keyboarding
LA Language Arts, English literature, and appropriate tools
MA Mathematics; filling in the specific area will narrow down this topic

NETS FOR TEACHERS— PREPARING TEACHERS TO USE TECHNOLOGY
343
APPENDIX D • EVALUATION FORMS
MC Multicultural
MM Multimedia Production
PS Problem Solving/Logic
PRO DEV Professional Development
RL Reference Library
SW School to Work; skills taught in school that directly translate into jobs
SC Science; filling in the specific topic will narrow down this subject
SS Social Studies; filling in the specific topic will narrow down this subject
SN Special Needs
TE Tests and Testing
WL World Languages (includes foreign language, American sign language, and ESL)
The grades are the standard grade levels; PK stands for prekindergarten.
6. Start using the technology resource. Examine it from the student’s point of view, making
mistakes and hitting wrong keys. Examine it from a teacher’s perspective, and compare what it
offers with what is needed in the classroom. Examine it as a supportive colleague and identify
how else the resource might be used (e.g., which other grades, topics, etc.).
7. You might want to begin with the “Technical Quality” section. This section is quite short. If the
program is not accessible, installable, or operational, then the evaluation is over. Be fair. If the
resource did not perform well because of limiting hardware, then note that exception. If you used
at least the minimum resources recommended by the publisher and the program still did not
perform well, then grade accordingly. In your grading on technical quality, indicate the way it
leaves your equipment when you’re done. Does your computer monitor suddenly show a new color
or a different resolution? Does the resource alter any settings without returning them to normal?
8. Under “Content,” list the objective set of guidelines you are using for comparison. If you are using
a curriculum guide that is in print, please state that information. For example, when examining a
math program you might be comparing the content to the NCTM Standards or your state
framework. List both and how well the software meets each.
9. Under “Assessment,” answer the questions: Did the resource provide guidelines or rubrics for
assessing student success? Are there pretests and posttests? Does the resource have built-in
features for students to express what they learn, such as a presentation component? If the
software allows students to print a report that could be used for assessment in a student portfolio,
include that information here.
10. The very first entry under the “Instructional Design” section is the most cryptic on the form. Mode
describes how the student uses the resource.
AC Accessibility: The software was written to provide access for students with special needs. For
example, it might provide a connection to an alternative input device.
AU Authoring System: These use a code of commands that enables a nonexpert to write
interactive programs. This mode also includes shell programs in which teachers insert their own
problems or data.
BL Bilingual: Verbal and/or written information or directions are available in more than one language.
CA Creative Activity: Programs with this designation have some structure or activity that
encourages students to exercise imagination and creativity.

344
NETS FOR TEACHERS— PREPARING TEACHERS TO USE TECHNOLOGY
APPENDICES
CP Computer Programming: This denotes a computer language or software-based activity for
teaching computer science or computer literacy classes.
DE Demonstration and Presentation: This is software used to present some aspect of the
curriculum or used to create a presentation of material, for example, to create slides using a
slideshow option.
DP Drill and Practice: These programs offer students unlimited practice on concepts they
presumably have already learned. A good drill and practice program provides feedback to
students, explains how to get the correct answer, and contains a management system to keep
track of student progress.
EG Educational Game: Usually these introduce drill and practice in a game format with a winner
or scoring system.
EX Exploration: Students can maneuver through a predesigned environment, testing and trying
various components of the environment.
GP Guided Practice: These offer students hints, assistance, and even reteaching as they practice a
concept.
IN Internet: The program directly connects to the Internet or World Wide Web. Some programs
function fully without currently being connected to the Internet but can be connected for
additional resources or interaction.
LEP Limited English Proficiency: This is software that can be used by students who have limited
English-speaking skills.
MM Multimedia: This software facilitates the development of multimedia presentations.
PS Problem Solving: These require student strategy and input. Most simulations (SI) and
educational games (EG) require some problem solving on the students’ part but may not have
PS in their mode listing.
RF Reference: These include electronic forms of traditional references, such as dictionaries,
thesauri, and encyclopedias, as well as extensive references on particular subjects.
SI Simulation: These programs create a world on the screen where realistic conditions apply and
students can see cause and effect, test hypotheses, and fix variables one by one.
TE Testing: Program tests students on subjects already taught, records their scores, and provides
the correct answer.
TL Tool: These include word processing, desktop publishing, database management, spreadsheets,
graphics, and telecommunications programs, and any software that students use to perform
a task.
TU Tutorial: The computer presents new concepts and skills through interactive text, illustrations,
descriptions, questions, and problems.

NETS FOR TEACHERS— PREPARING TEACHERS TO USE TECHNOLOGY
345
APPENDIX D • EVALUATION FORMS
11. Under the list of items the resource promotes, add your own criteria. Or change the beginning
term from promotes to provides and fill in your descriptors, such as remediation, practice,
reinforcement, new information, application, and so on.
12. Identify all of the four classic “Motivational” features that apply to this resource.
13. Complete the “Strengths” and “Weaknesses” sections.
14. Complete the section that begins “Describe the learning strategy incorporated in the design”
with a description of the resource in educational terms.
15. Complete your recommendation. Publishers tend to lump everyone under the word “user” when
describing how a resource can be used in the classroom. Please use educational terms; specify if
you are referring to students, teachers, or a group of students, for instance.
16. After all of the sections have been filled in and additional comments supplied, grade the
resource. The final rating should not be an average of the grades but a combined grade based on
both the scores and the importance of the criteria. For examples, if a resource scores an F on
technical quality, then even the best instructional design may not be deliverable to the student,
thus the overall rating of F. Or a resource might be excellent in every category but based on
flawed content or outdated premises, thus rendering it useless in the classroom.
17. Now for the acid test of both the resource and the report. Take both into the classroom. Use the
technology resource with students and modify the report based on your observations and
interviews with students.